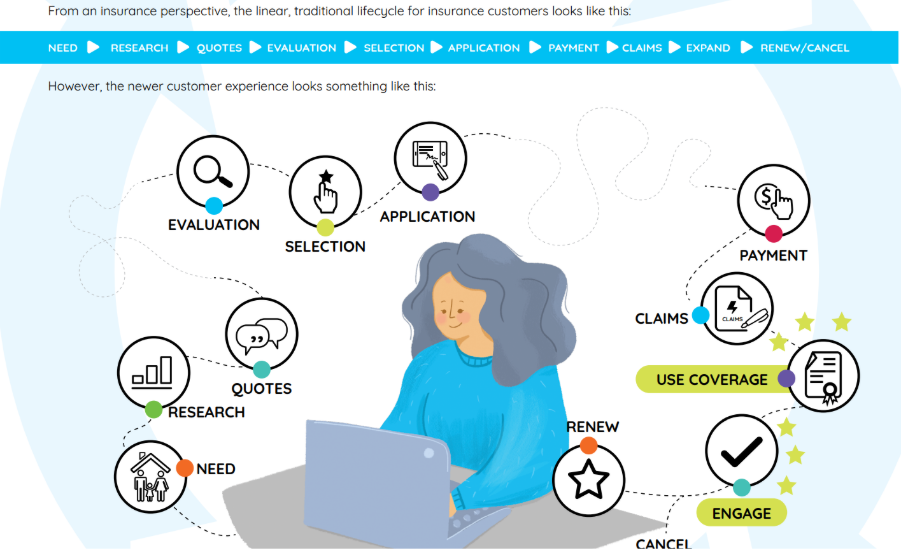
They say that a failure to plan is just planning to fail. Nowhere is that truer than when it comes to creating an allowance for doubtful accounts (AFDA). Without it, bad debt can blindside your finance team and leave you strapped for cash. By factoring in this allowance, you can account for the risk of bad debt while creating an accurate cash flow forecast.
In this blog, you'll learn
- What is a doubtful account
- Why track doubtful accounts
- Doubtful accounts vs bad debt
- What is allowance for doubtful accounts
- How to estimate doubtful accounts
- How to record allowance for doubtful accounts
- Late payment stats by industry
What is a doubtful account?
A doubtful account or doubtful debt is an account receivable that might become a bad debt at some point in the future. If customers purchase on credit, establishing an allowance of doubtful accounts is an important tool for your balance sheet and income statement.
Your accounts receivables team may not know which specific will go unpaid, but with a historical record and good forecasting, they can anticipate approximately how much potential revenue will become bad debt.
Why track doubtful accounts?
Doubtful accounts can turn into bad debt, and bad debt impacts your business’ bottom line. The ability to accurately forecast and account for bad debt means you have better insight into your working capital - and the health of your business.
Allowances for doubtful accounts also function as a safety net for your organization. It helps you anticipate the possibility of late or partial payments, or even the risk of a customer declaring bankruptcy. By factoring in these potential risks, CFOs can more effectively project budgets and plan investments.
Doubtful account versus bad debt
A bad debt is an account receivable that has been clearly identified as not being collectible, and should be written off at once. A doubtful debt is an account receivable that might become a bad debt but it’s not certain if or when that will happen.
What is allowance for doubtful accounts?
To account for the doubtful debt (or doubtful accounts), you create an allowance, which is recorded on your balance sheet. The balance sheet presents your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. An allowance for doubtful accounts reduces your reported amount of accounts receivables.
An allowance for doubtful accounts is established in a reserve account (also known as a contra account) that reduces your accounts receivables, so it is recorded under assets, as a reduction after the accounts receivables line. Estimate the amount of accounts receivables that may become bad debts over a given period of time, and enter a credit of that amount in your reserve account: this is your allowance of doubtful accounts.
In simple terms, in your double-entry books, debit your bad debts expense account and credit your allowance of doubtful accounts. When there is a bad debt, debit your allowance of doubtful accounts and credit your accounts receivable account.
For example: Company XYZ has $200,000 of accounts receivable, of which it estimates that $10,000 will eventually become bad debts. It therefore charges $10,000 to the bad debt expense (which appears in the income statement) and a credit to the allowance for doubtful accounts (which appears just below the accounts receivable line in the balance sheet). A month later, XYZ knows that a $2,000 invoice is indeed a bad debt. It creates a credit memo for $2,000, which reduces the accounts receivable account by $2,000 and the allowance for doubtful accounts by $2,000.
So, when XYZ recognizes the actual bad debt, there is no impact on the income statement - only a reduction of the accounts receivable and allowance for doubtful accounts line items in the balance sheet, and those offset each other.
Featured Resource: The AR Collections Playbook

How to estimate your doubtful accounts
Historical percentage method
One common way to estimate how much your allowance for doubtful accounts should be is to rely on historical data. If your business was steady in the year prior and you do not anticipate significant changes to your business in the upcoming months, this is a simple and fast way to look at it.
Accounts receivable aging method
Another method is to use your aging receivables. In this method you would group your aging receivables and determine the percentage for each group that is likely to become uncollectible.
For example:
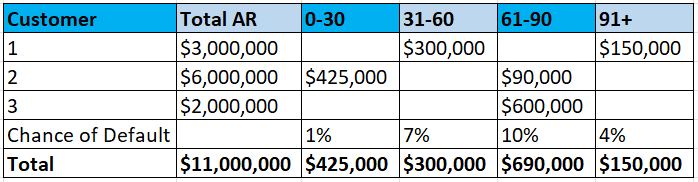
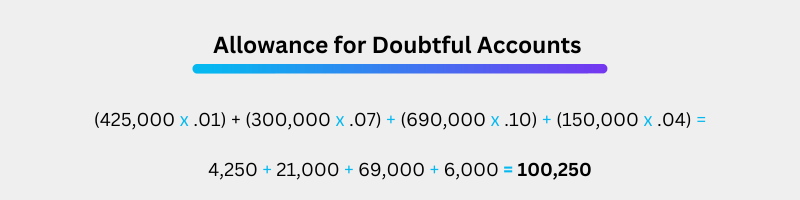
The last step is to find the recorded AR, so take the total AR and subtract it from the allowance for doubtful accounts (11,000,000 - 100,250). This leaves a recorded AR of $10,899,750.
The allowance for doubtful accounts helps report the bad debt expense as soon as the estimate is calculated and portrays a more accurate view of the financial statements. Tracking those doubtful accounts also gives you insight into your customer base, and which segments may be higher risk for you - therefore altering your target market or credit management processes to ensure your business is protected. For both financial compliance and business health reasons, managing your doubtful accounts is important in your business.
How to record allowance for doubtful accounts
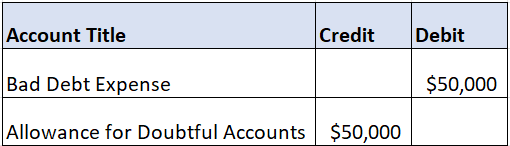
How you document your allowance for doubtful accounts is almost as important as calculating them correctly. The allowance is paired with bad debt in your account books. Because of this, you must debit the latter when recording the allowance. You then deduct the allowance from your overall receivables balance when calculating the total asset value of the receivables on your balance sheet.
As an example, let’s assume that your organization earned $1,000,000 in sales for a given accounting period, and you’ve estimated a bad debt rate of 5%. That creates a bad debt budget of $50,000. You would enter that figure as a debit and offset it by crediting an allowance in the same amount.
Is allowance for doubtful accounts an asset or liability?
Allowance for doubtful accounts are considered an asset, not a liability. However, they are listed as a contra-asset. A contra-asset account is defined as an asset account in which the natural balance of the account will either be a zero or a credit (negative) balance. Other examples of contra-assets include accumulated depreciation, accumulated impairment losses, sales discounts, and sales returns.
Doubtful account allowances by industry
The allowance for doubtful accounts that you set up will largely be contingent on industry. While there is no set standard to follow, a general rule of thumb is that the longer your collection cycle, the greater allowance you should account for.
With that in mind, it's helpful to take a look at late payment statistic by industry to gain an idea of where your organization falls.