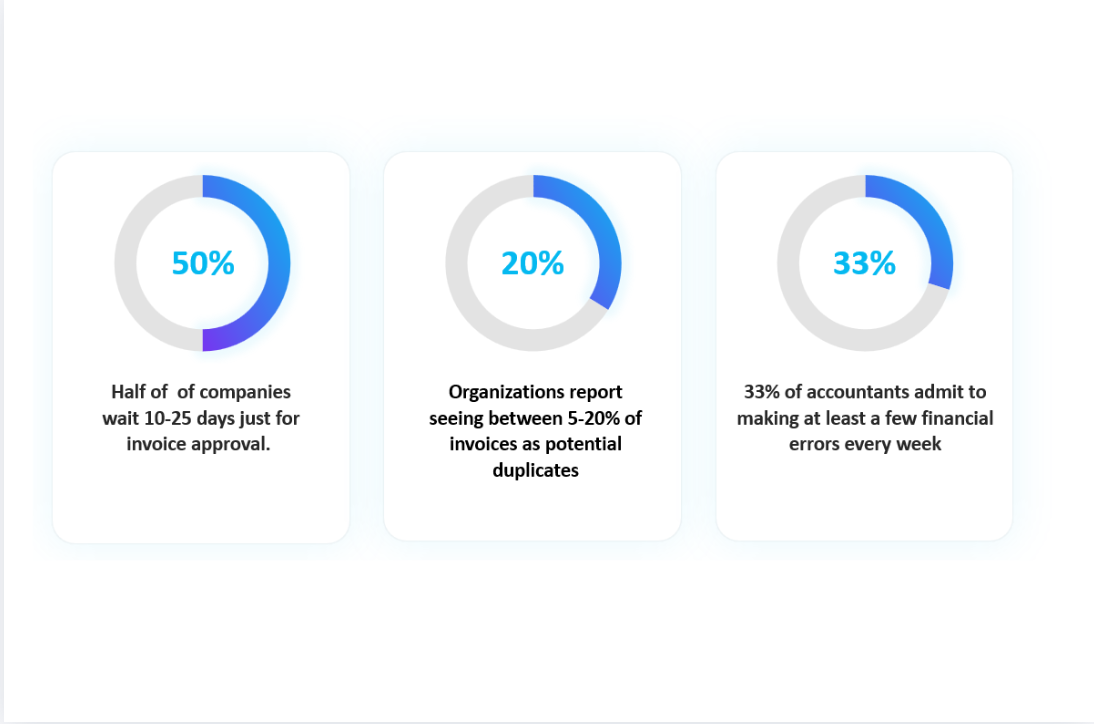
Introduction
Accounts receivable (AR) is more than just chasing payments. It’s about making sure your business gets paid, stays liquid, and keeps customers in the loop.
Every company that sells on credit needs a way to track invoices and collect what’s owed. That’s what accounts receivable management does. It helps you stay organised, keep cash coming in, and spot issues before they turn into real problems.
Still, a lot of businesses hit the same snags: late payments, cash flow gaps, billing mistakes, and no clear view of what’s overdue. These slow down collections and lead to write-offs that hurt your bottom line.
But this doesn’t have to be the norm. A better AR process—especially one backed by automation—can help you get paid faster, reduce disputes, and keep things running smoothly. That’s what this guide is here to help you do.
What is accounts receivable management?
Accounts receivable management is the process of overseeing, tracking, and collecting money owed to a business for goods or services sold on credit. It ensures that customer invoices are accurate, sent on time, and paid within agreed terms. Done well, AR management improves a company’s cash position, reduces financial risk, and supports stronger customer relationships.
AR management is a core component of the broader order-to-cash cycle—the end-to-end process that starts when a sale is made and ends when payment is received and recorded. While sales, order fulfillment, and billing all play important roles, accounts receivable is where revenue becomes cash. Any delays or breakdowns here can stall the entire cycle and hurt cash flow.
Key functions of AR management
Accounts receivable management includes several interconnected tasks that keep the payment process running smoothly:
- Credit approval and onboarding: Assessing credit risk and setting payment terms before a sale
- Invoice generation and delivery: Creating clear, accurate invoices and sending them promptly
- Payment tracking and reminders: Monitoring payment status, following up on due dates, and recording receipts
- Collections and dispute resolution: Handling customer disputes, resolving deductions, and recovering overdue amounts
- Reporting and performance metrics: Using data to track days sales outstanding (DSO), aging reports, and cash flow impact
What does accounts receivable manage?
Accounts receivable handles short-term receivables, which are money customers owe for recent purchases. It keeps tabs on the timing and accuracy of payments, ensuring customers stick to agreed-upon terms. AR systems also flag overdue accounts and credit risks so teams can act before minor delays become significant issues.
AR is also responsible for handling communication related to payments. This involves sending reminders, resolving discrepancies, and providing customers with tools such as portals and online payment options to ensure the process is as seamless as possible.
The role of AR in business health
AR management directly impacts a company’s financial stability. By keeping payments timely and receivables in check, businesses improve their working capital—the cash available to fund operations, pay vendors, and invest in growth.
It also decreases the risk of bad debt by identifying slow payers early and implementing consistent credit policies. Additionally, because clear communication and dependable processes foster trust, it improves customer satisfaction, which can result in repeat business and stronger relationships over time.
In short, AR management is not just a financial task—it’s a business-critical function that affects everything from cash flow to customer loyalty.
The five steps to managing accounts receivable
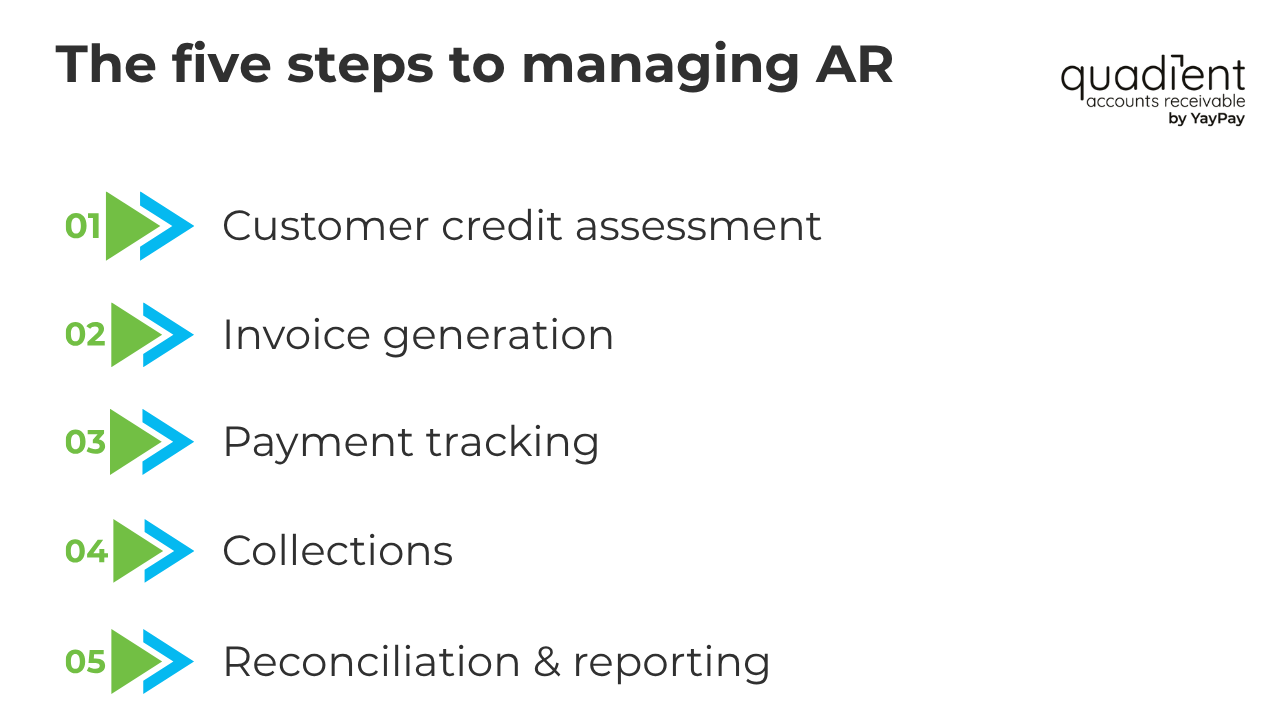
Step 1: Customer credit assessment and approval
Evaluate each customer’s creditworthiness before extending credit, using credit history, payment behaviour, trade references, and credit bureau data. Set appropriate credit limits and terms based on risk. This step helps reduce exposure to bad debt and ensures customers are set up with payment terms they can meet.
Step 2: Invoice generation and delivery
Standardise invoice templates and ensure invoices are accurate, timely, and easy to read. Include payment terms, due dates, and payment instructions. Use automated invoicing software to streamline the process and offer electronic invoice presentment and payment (EIPP) to improve speed and convenience.
Step 3: Payment tracking and reminders
Use AR dashboards to track which invoices have been paid, which are overdue, and which are approaching their due dates. Set up automated reminders to reduce follow-up time and nudge customers before payments are late. This helps reduce days sales outstanding (DSO) and avoid unnecessary collection efforts.
Step 4: Collections and follow-up
When payments are late, your collections process should be clear and consistent. Start with automated dunning emails or phone calls. Escalate based on internal thresholds and involve third-party collections only when needed. Segment accounts by risk level to prioritise follow-up effectively.
Step 5: Reconciliation and reporting
Match incoming payments to the correct invoices and resolve discrepancies quickly. Regular reconciliation helps maintain clean financial statements and minimises errors. Monitor AR metrics such as aging reports, AR turnover ratio, and DSO to monitor performance and spot issues early.
How to improve accounts receivable management
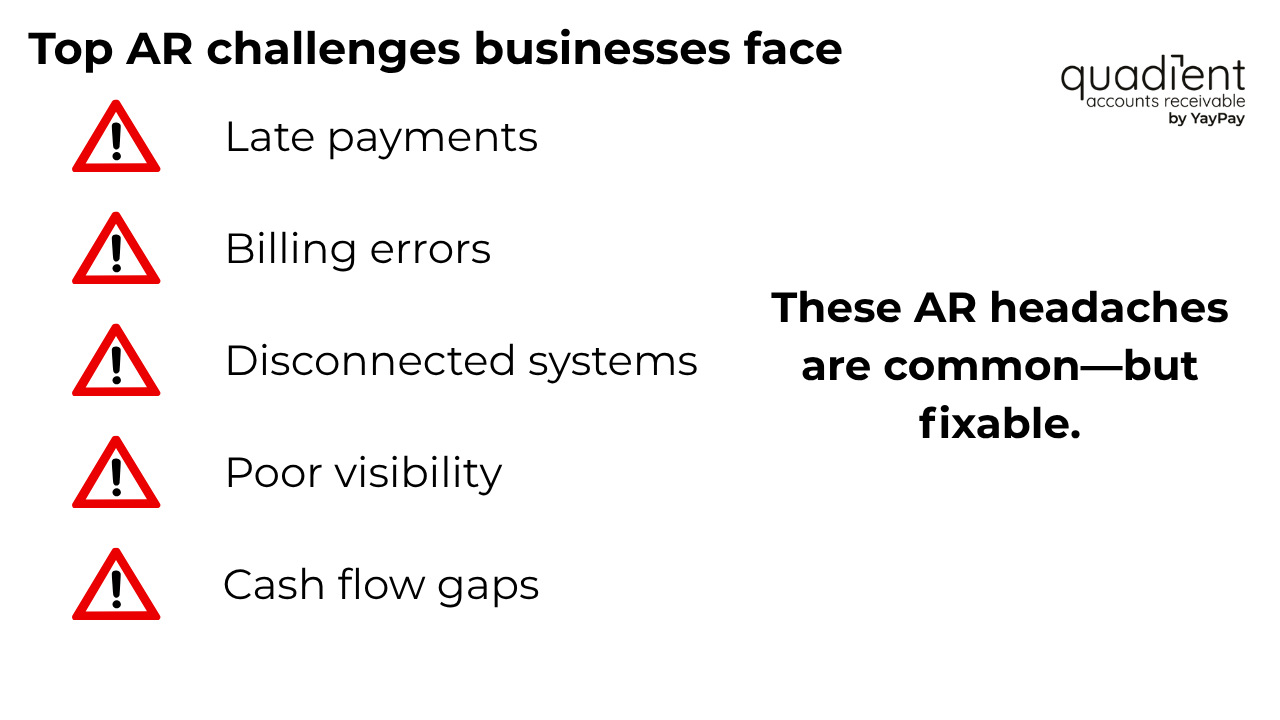
Identify your biggest AR pain points
Start by mapping your current AR process and identifying where delays or errors occur most frequently. Common issues include:
- Long DSO and frequent overdue payments
- Inconsistent follow-up and manual workflows
- Incomplete or outdated customer data
- Billing disputes caused by unclear or inaccurate invoices
- Limited real-time visibility into AR performance
Practical ways to improve your AR process
- Segment customers by payment risk and behaviors
- Automate invoicing and payment reminders to reduce manual tasks
- Offer flexible payment options like ACH, credit card, and digital wallets
- Use a customer portal to allow self-service payments and invoice access
- Set and enforce clear payment terms on every invoice
- Provide incentives for early payments, such as small discounts
- Keep customer master data up to date for accurate billing
- Introduce automated workflows for approvals, reminders, and collections
AR metrics that matter
Tracking the right performance metrics is critical for optimizing AR. Focus on:
- DSO – How long it takes to collect
- Accounts receivable turnover ratio – How often receivables are converted to cash
- Percentage of overdue receivables – A leading indicator of collection health
- Bad debt ratio – Helps assess risk and credit policy effectiveness
- Cash conversion cycle – Measures how quickly cash flows through the business

The role of accounts receivable management software
What is AR management software?
AR management software centralises and automates the accounts receivable process. It integrates with your accounting, billing, ERP, and CRM systems to improve accuracy and reduce manual work.
Core features
- Automated invoice creation and delivery
- Online payment portals and processing
- Payment tracking and real-time aging dashboards
- Automated dunning workflows and follow-ups
- Dispute and deduction management
- Self-service customer portals
- Real-time analytics and reporting
- Credit limit and credit approval automation
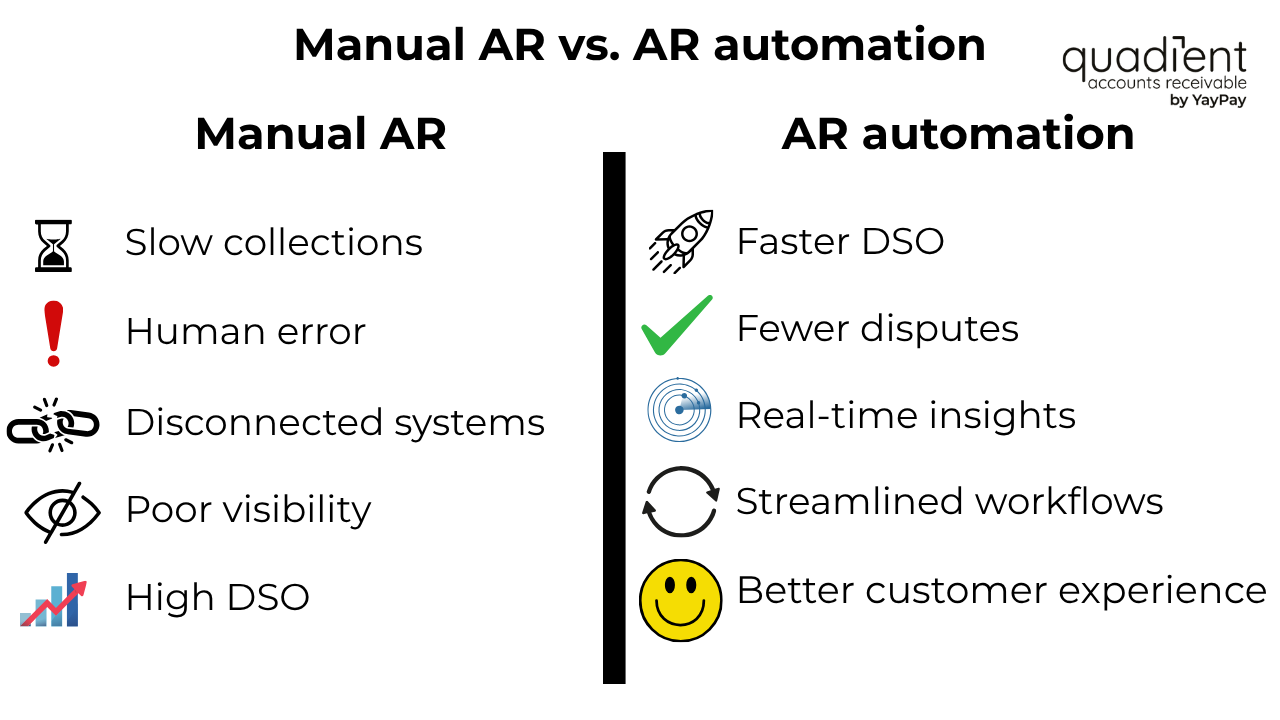
Benefits of AR software
- Faster collections and reduced DSO
- Fewer errors and billing disputes
- Improved visibility into receivables and payment trends
- Higher productivity from AR teams
- Better customer experience and communication
- More accurate cash flow forecasting
- Easier compliance with audit and reporting requirements
Tips to manage AR effectively
Improving accounts receivable management doesn’t always require a complete system overhaul. Often, small, consistent actions have the most significant impact. The key is to be proactive and intentional. The tips and checklist below offer practical steps any AR team can use to manage receivables more effectively and keep cash flow steady.
Actionable tips
- Use automation tools for invoicing, reminders, and tracking. Learn more about AR automation.
- Monitor key metrics like DSO weekly, not monthly
- Communicate clearly across finance, sales, and customer service
- Standardise your credit policy and train your team to enforce it
- Review and adjust credit terms based on customer payment history
- Audit your AR process regularly to find gaps and inefficiencies
Checklist
- Establish a written AR policy
- Automate core functions like reminders and invoicing
- Track key metrics such as DSO and aging reports
- Follow up quickly on delinquent accounts
- Evaluate and update credit limits periodically
- Offer digital payment options and a customer portal
- Use AR software to eliminate manual errors and delays
- Train staff on tools, process changes, and customer communication best practices
Conclusion: The road to better accounts receivable
Strong AR management is a strategic asset that keeps your business financially stable, your operations funded, and your customer relationships intact.
By taking control of your AR process and implementing the right tools, you can reduce late payments, improve working capital, and boost overall efficiency. AR automation software is essential for managing credit risk, streamlining collections, and supporting growth.
Next steps:
- Review your current AR setup and identify gaps
- Explore AR automation tools that integrate with your existing systems
- Start small: automate reminders, standardise invoices, and track DSO weekly
- Invest in the metrics and technology that will drive long-term improvements